In today’s technologically driven world, cables form the lifelines connecting our devices, homes, and industries. The manufacture of these cables involves a meticulous and sophisticated process known as cable extrusion. This technique is crucial for producing the various types of cables we rely on daily, from the simple electrical wires in our homes to the complex fiber optic cables enabling global internet connectivity. Understanding the cable extrusion process not only sheds light on the intricacies of cable production but also highlights the innovative engineering behind it.
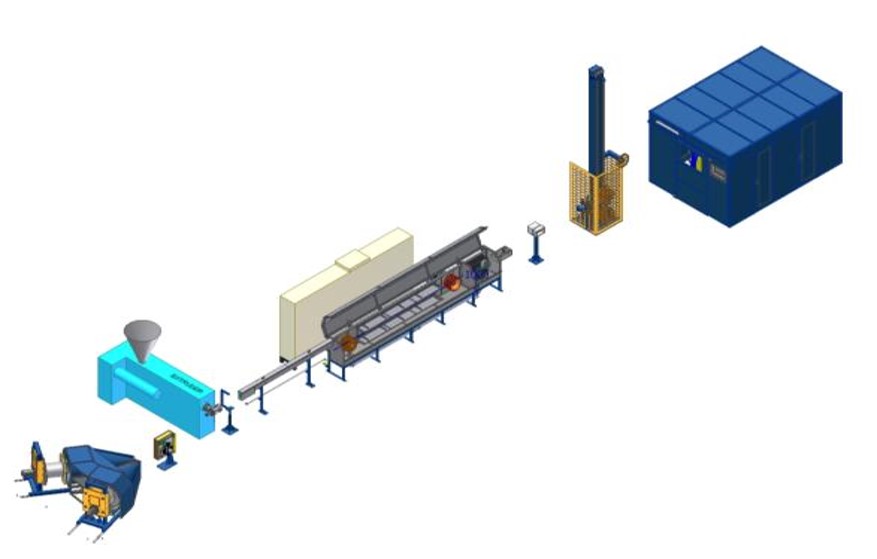
insulation line
You may be interested in this article. The Latest Tech Trends in Cable Manufacturing Equipment
What is Cable Extrusion?
Cable extrusion is a manufacturing process used to produce continuous lengths of cable and wire by forcing raw material, typically plastic or metal, through a shaped die to create a specific cross-sectional profile. The process is akin to squeezing toothpaste out of a tube, albeit with far more precision and complexity. The material emerges from the die in a continuous stream, forming the desired shape as it cools and hardens.
The Importance of Cable Extrusion
The significance of cable extrusion in modern manufacturing cannot be overstated. This process ensures that cables meet stringent quality standards for electrical performance, durability, and safety. Whether for telecommunications, power distribution, or data transmission, cable extrusion allows for the consistent production of high-quality cables essential for reliable operation in various applications.
Key Components of the Cable Extrusion Process
- Raw Material Preparation**: The process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include copper for electrical conductivity and polymers like PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PE (polyethylene), or XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene) for insulation. These materials must be of high purity and specific formulations to meet the required standards.
- Feeding System**: The prepared raw materials are fed into the extrusion machine’s hopper. The hopper controls the flow of material into the extruder, ensuring a consistent and continuous feed, which is critical for maintaining the quality of the extruded cable.
- Extruder Machine**: The heart of the extrusion process is the extruder machine. This machine comprises several key parts:
* Screw: A rotating screw inside a heated barrel that pushes the material through.
* Heated Barrel: The barrel heats the material to its melting point, making it pliable enough for extrusion.
* Die: A specially designed tool that shapes the material as it is forced through. The die’s design determines the cable’s final cross-sectional shape. - Cooling System: Once the material exits the die, it is immediately cooled to solidify its shape. This is typically done using water baths or air cooling systems, depending on the material and desired properties of the finished cable.
- Pulling and Winding: The extruded cable is then pulled through the cooling system by a capstan or take-up device, ensuring it maintains its shape and consistency. Finally, the cooled and solidified cable is wound onto reels or spools for storage and transportation.

The Steps of the Cable Extrusion Process
- Material Loading: The process begins with loading the raw material into the hopper. This material is typically in pellet or powder form and must be carefully measured to ensure consistency.
- Melting and Mixing: As the material enters the extruder barrel, it is heated and mixed by the rotating screw. The temperature and speed must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired viscosity and homogeneity.
- Extrusion Through the Die: The molten material is then forced through the die, shaping it into the desired cable form. The die must be precisely engineered to produce cables with exact dimensions and characteristics.
- Cooling and Solidification: The freshly extruded cable passes through a cooling system, which rapidly solidifies the material to retain the shape imparted by the die. The cooling process must be carefully controlled to avoid internal stresses and defects.
- Pulling and Inspection: The solidified cable is continuously pulled through the cooling system to maintain a consistent extrusion speed and diameter. Throughout this stage, the cable undergoes rigorous inspection for any surface defects or dimensional inconsistencies.
- Winding and Packaging: Finally, the finished cable is wound onto spools or reels, ready for quality testing, packaging, and shipment.
Types of Cable Extrusion Processes
- Single Extrusion: This process involves extruding a single layer of material around a conductor. It is commonly used for simple cables requiring basic insulation.
- Co-extrusion: Co-extrusion involves extruding multiple layers of different materials simultaneously. This technique is used to produce cables with enhanced properties, such as improved insulation, shielding, and strength.
- Triple Extrusion: In triple extrusion, three layers are extruded simultaneously, often involving a conductor, insulation, and a protective outer jacket. This process is typical in high-performance cables, such as those used in harsh environmental conditions.

Advantages of Cable Extrusion
- Customization: Cable extrusion allows for precise control over the cable’s dimensions, materials, and properties, enabling the production of custom cables tailored to specific applications.
- Efficiency: The continuous nature of the extrusion process makes it highly efficient, capable of producing large quantities of cable with minimal waste.
- Quality Control: Advanced monitoring and control systems ensure consistent quality throughout the extrusion process, resulting in reliable and high-performance cables.
- Versatility: Cable extrusion can accommodate a wide range of materials and configurations, making it suitable for diverse industries, including telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and energy.
Challenges in Cable Extrusion
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials for specific applications can be challenging, requiring a deep understanding of material properties and performance requirements.
- Die Design: Designing the extrusion die requires precision engineering and extensive testing to ensure the desired cable characteristics are achieved.
- Process Control: Maintaining consistent temperature, pressure, and speed throughout the extrusion process is crucial for producing defect-free cables. This necessitates sophisticated control systems and regular maintenance.
- Environmental Factors: External factors such as ambient temperature and humidity can impact the extrusion process, requiring careful monitoring and adjustment.
Future Trends in Cable Extrusion
The cable extrusion industry continues to evolve with advancements in materials, technology, and processes. Key trends include:
- Sustainable Materials: Increasing focus on sustainability is driving the development of eco-friendly materials and processes, reducing the environmental impact of cable production.
- Smart Manufacturing: The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence), is enhancing process control, efficiency, and quality in cable extrusion.
- High-Performance Cables: As demand for high-speed data transmission and renewable energy grows, there is a corresponding need for advanced cable designs capable of withstanding higher voltages, temperatures, and environmental stresses.
- Miniaturization: The trend towards smaller, more compact devices is driving the development of miniaturized cables with enhanced performance characteristics.

You may be interested in this article. Essential Maintenance Tips for Cable Manufacturing Machines
Conclusion
The cable extrusion process is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of reliable, high-quality cables that power our daily lives. By understanding the intricacies of this process, we gain insight into the sophisticated engineering and innovation behind the cables that connect our world. As technology continues to advance, the cable extrusion industry will undoubtedly evolve, embracing new materials, processes, and technologies to meet the ever-growing demands of our interconnected society.
Discover Excellence with Frekans Machine’s Cable Extrusion Line
Are you seeking a reliable partner for top-notch cable manufacturing? Look no further than Frekans Machine, the industry leader in producing high-quality Cable Extrusion Lines. Our state-of-the-art machinery ensures precision, efficiency, and unparalleled performance in every meter of cable produced.
At Frekans Machine, innovation meets craftsmanship. Our Cable Extrusion Lines are meticulously engineered to handle a wide range of materials, ensuring your cables meet the highest standards of durability and electrical performance. Whether you’re in telecommunications, power distribution, or any other industry requiring premium cables, our machines are designed to deliver excellence consistently.
Why choose Frekans Machine? Because we don’t just build machines; we build trust and partnerships. Our commitment to quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous innovation sets us apart. With Frekans Machine, you gain more than just a supplier—you gain a dedicated ally in your production process.
Ready to revolutionize your cable manufacturing? Contact Frekans Machine today and experience the future of cable extrusion. Let’s create something extraordinary together!
Reach out to us at contact information or visit our website at https://www.frekansmakina.com.tr/. Your journey to superior cable production starts here with Frekans Machine.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Cable Extrusion Process
Several advancements are driving the future of the cable extrusion industry:
- Sustainable Materials: There is an increasing focus on developing eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce the environmental impact of cable production.
- Smart Manufacturing: The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is enhancing process control, efficiency, and quality in cable extrusion.
- High-Performance Cables: Growing demand for high-speed data transmission and renewable energy is leading to the development of advanced cable designs capable of withstanding higher voltages, temperatures, and environmental stresses.
- Miniaturization: The trend towards smaller, more compact devices is driving the development of miniaturized cables with enhanced performance characteristics, meeting the needs of modern electronic devices and systems.
The main challenges in the cable extrusion process include:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials to meet specific application requirements can be complex and requires in-depth knowledge of material properties.
- Die Design: Precision in die design is essential for achieving the desired cable characteristics, necessitating thorough testing and engineering.
- Process Control: Maintaining consistent temperature, pressure, and speed throughout the extrusion process is vital for producing defect-free cables, requiring sophisticated control systems.
- Environmental Factors: External conditions like ambient temperature and humidity can impact the extrusion process, necessitating careful monitoring and adjustment to maintain product quality.
The extrusion die is a critical component in the cable extrusion process. It shapes the raw material as it is forced through, determining the final cross-sectional profile of the cable. The die must be precisely engineered to produce cables with exact dimensions and characteristics. Any deviation in the die design can lead to defects and inconsistencies in the finished product. Therefore, extensive testing and precision engineering are required to ensure the die produces high-quality cables.
Common materials used in cable extrusion include:
- Copper: Widely used for its excellent electrical conductivity.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): A versatile polymer used for insulation and jacketing due to its durability and flexibility.
- PE (Polyethylene): Known for its good insulation properties and resistance to moisture.
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): Offers superior thermal and electrical properties, making it ideal for high-performance cables. These materials must be of high purity and specific formulations to ensure the desired cable characteristics and performance.
The cable extrusion process is used to manufacture continuous lengths of cable and wire by forcing raw materials through a shaped die to create specific cross-sectional profiles. This process ensures the cables meet stringent quality standards for electrical performance, durability, and safety. It’s crucial for producing various types of cables used in telecommunications, power distribution, and data transmission.



